Cardiac Tamponade
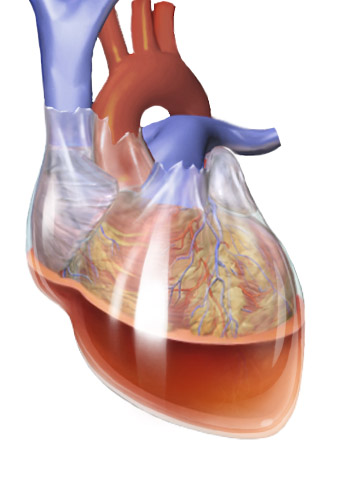
This illustration shows cardiac tamponade, a condition where the pericardium becomes filled with blood (hemopericardium), compressing the heart and impairing its function.
Image by BruceBlaus, licensed under CC BY 3.0. Cited from: Blausen.com staff (2014). "Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014". WikiJournal of Medicine, 1(2). DOI: 10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436.
Definition
Cardiac tamponade is a medical condition in which fluid accumulates in the pericardial space surrounding the heart. This is a medical emergency because the heart is experiencing increased pressure as a result of build or build. Without treatment, cardiac tamponade can be fatal.
Aetiology
Acute causes:
Chest trauma/injury
Idiopathic (no known causes)
Myocardial infarction (MI)
Pericarditis
Heart surgery generally caused by a post-surgical complications
Chronic causes:
Cancer.
CKD related uremia
Connective tissue disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and Lupus.
Tuberculosis (TB): a complication from TB.
Pathophysiology
The accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space raises the heart's intracardiac pressure, impairing its ability to pump blood. Additionally, there is a decrease in blood flow through the heart.
Risk factors
Pericarditis: Individuals with a history of previous pericarditis (inflammation of the pericardium)
Cancer
Heart failure
Kidney failure
Radiation therapy: radiation therapy performed around the heart area
Sign and symptoms
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Weakness
Dizziness
Investigations
Diagnosis starts with a physical examination of the patient and a good history.
Investigations may include:
ECG
CXR - fluid in the pericardial space can be observed
ECHO
CT SCAN
MRI
Cardiac catheterisation
Culture of fluid from a pericardiocentesis
Management
Medical emergency - patient must be admitted to the hospital
Pericardiocentesis: drainage of fluid in the pericardial space through a needle or a catheter inserted through the chest into the pericardial space.
Treat underlying causes such as TB, pericarditis, MI etc.
Check out our youtube channel
Blueprint Page
Explore the comprehensive blueprint for Physician Associates, covering all essential topics and resources.
Book Your Session
Enhance your skills with personalised tutoring sessions tailored for Physician Associates.

